Types of Delusions
Feb 10, 2024 By Marie White
Do you ever wonder what makes some people think their thoughts are reality? Or why certain individuals can't distinguish between what is real and what isn't? It might surprise you that those behaviors and perceptions aren't just signs of a wild imagination - they could be a symptom referred to as delusions.
Delusions refer to false beliefs that an individual believes passionately, despite evidence or proof from others attempting to disprove these beliefs. Today we will dive into various types of delusions to better understand how they affect one's life, behavior, and overall mental health.
Categories Of Delusion

Categories of delusions are determined based on the specific characteristics of each delusion. Delusions can be split into four categories: Bizarre, Non-Bizarre, Mood-Congruent, and Mood-Neutral. Each category has its own set of unique features that helps to distinguish it from other types of delusions.
Bizarre Delusion
Bizarre delusions are the most unusual and implausible of all delusion types. These delusions typically involve something impossible or highly improbable, such as believing aliens have abducted you or that secret agents are following you. Bizarre delusions often have no basis in reality and may not be shared by anyone else in your social circle.
Non-Bizarre Delusion
Non-bizarre delusions are more plausible than bizarre ones and may be based on actual events. These delusions often involve paranoia, such as a fear of being followed or watched, and they may also involve exaggerated beliefs about your power or importance.
Unlike bizarre delusions, non-bizarre delusions are considered to be more widely shared among people in the same social circle.
Mood-Congruent Delusion
Mood-congruent delusions are those that are consistent with either a depressed mood or an elevated (manic) mood. For example, someone experiencing a depressive episode may have delusions of persecution—believing others are unfairly targeting them—whereas someone in a manic state may have delusions of grandeur—believing they have special powers or are destined for greatness.
Mood-Neutral Delusion
Mood-neutral delusions are not influenced by either a depressed or elevated mood. These delusions often involve bizarre beliefs, such as believing that you can read other people's thoughts or that someone has replaced your family with clones. Mood-neutral delusions may also involve underlying persecution, conspiracy, and paranoia themes.
Types of Delusions
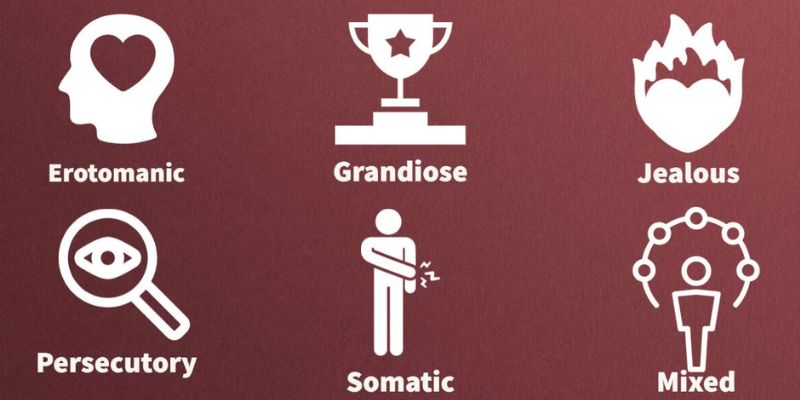
Persecutory delusion
Persecutory delusion is a delusional disorder in which the individual believes they are being targeted, followed, or harassed by an individual or group. This delusion can cause fear, paranoia, and physical symptoms such as increased heart rate, sweating, and nervousness.
Persecutory delusions often involve themes of suspicion that someone is out to get the individual, and they may believe that their enemies are conspiring against them. The individual may also be convinced that their conversations are being monitored or that they're being watched from afar.
Such feelings of paranoia can lead to a sense of isolation and desolation as the individual begins to build walls around themselves to protect themselves from further harm. People experiencing persecutory delusions may find themselves avoiding public places and will take measures to limit their exposure to those they believe are out to hurt them.
Friends, family, and healthcare professionals need to be aware of the signs of persecutory delusions so that appropriate support can be provided. Cognitive-behavioral therapy and cognitive restructuring techniques can help an individual identify distortions in thinking and replace them with more helpful ways of thinking.
Grandiose delusion
Grandiose delusion is a delusional disorder in which the individual believes they are superior to those around them or have special abilities that no one else has. Grandiose delusions often involve themes of power, grandeur, wealth, fame, beauty, and invincibility.
Individuals with grandiose delusions may believe that they have superpowers or are celebrities, and they may take extreme measures to prove their greatness, such as buying expensive cars or jewelry. Grandiosity can lead to feelings of superiority and a disregard for the feelings and opinions of others, which can lead to problems in relationships.
People experiencing grandiose delusions often have a distorted sense of self-worth and may not recognize the need for help or support from others.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy can be beneficial in helping to identify underlying causes of grandiosity and replace them with more helpful ways of thinking. Additionally, medications like antipsychotics can be used to help manage symptoms associated with delusion.
Delusional jealousy
Delusional jealousy is a delusion in which the individual believes their partner is engaging in romantic or sexual activities with someone else. This delusion can cause intense insecurity and fear, leading to relationship problems such as arguments, distrust, and even physical violence.
Individuals experiencing delusional jealousy may become preoccupied with their partner's behavior and question them incessantly about their whereabouts, activities, and relationships. They may also become suspicious of any contact their partner has with other people, leading to feelings of mistrust and possessiveness.
Erotomania or delusion of love
Erotomania, also known as Delusion of Love, is a type of delusion in which an individual believes someone is in love with them. The individual may believe that the person loves them deeply and has a strong emotional connection to them, even though no evidence supports this belief.
This belief can lead to intrusive behavior such as sending unwanted letters or gifts, making unwanted phone calls or visits, and even stalking the person they believe is in love with them.
Erotomania can be caused by mental health conditions such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. It can also be caused by feelings of social isolation, low self-esteem, difficulty forming relationships, traumatic experiences from past relationships, and a fear of abandonment.
Erotomania can have serious psychological, social, and legal implications. People experiencing this delusion may become fixated on the object of their affection and may make decisions or take actions that put their safety at risk.
Somatic delusional disorder
Somatic delusional disorder is a type of delusional disorder in which an individual believes their body has changed somehow, usually resulting from a physical or medical condition. Individuals with somatic delusions may believe they have abnormalities such as tumors, diseases, parasites, or deformities.
Common symptoms of somatic delusion include:
- Excessive anxiety about one's health.
- Preoccupation with a particular part of the body (or body system).
- An obsession with seeking medical attention or self-diagnosing.
The cause of somatic delusional disorder is unknown, but several theories exist, including genetic factors and psychological trauma. It is believed that individuals may be predisposed to this condition due to their family history, and psychological trauma may trigger the onset of symptoms.
Induced delusional disorder or folie a' deux
Induced delusional disorder, also known as folie a deux, is a rare condition in which two or more people share the same delusion. It most commonly occurs between family members or intimate partners who are closely connected and have similar backgrounds.
In some cases, one person will exhibit symptoms of delusional thinking that the other's beliefs can influence. This delusion is usually temporary and will dissipate when the two people are separated.
FAQs
What are the 2 most common types of delusions?
The two most common types of delusions are persecutory delusion and grandiose delusion.
What causes delusional thinking?
Delusional thinking can be caused by various factors, including mental health conditions such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, feelings of social isolation, low self-esteem, difficulty forming relationships, traumatic experiences from past relationships, and fear of abandonment. Additionally, certain medications and drugs can also induce delusional thinking.
What are the treatment options for delusion?
Treatment for delusions typically involves a combination of medication and psychotherapy. Cognitive-behavioral therapy can be beneficial in helping to identify underlying causes of delusion and replace them with more helpful ways of thinking. Additionally, medications like antipsychotics can be used to help manage symptoms associated with delusion.
Conclusion
Delusions are a common mental health issue with various causes and effects. Types of delusions include persecutory delusion, grandiose delusion, delusional jealousy, erotomania or delusion of love, somatic delusional disorder, and induced delusional disorder or folie a deux. Understanding the different types of delusions can help individuals recognize them in their own lives and seek treatment if necessary.
-
 Fitness Nov 21, 2023
Fitness Nov 21, 2023Exploring the Benefits of a Juice Cleanse
Discover the objective and possible advantages of a juice cleanse, a popular health practise that involves drinking fresh juices for a specific time.
-
 Condition Oct 19, 2023
Condition Oct 19, 2023Can Booster Shots Affect Your Body Negatively?
New COVID-19 booster injections from Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna have been improved to target circulating coronavirus strains better and are expected to expand further this fall and winter. The modernized boosters are nearly indistinguishable from the ones that were available before they were pulled off shelves a year ago
-
 Condition Nov 20, 2023
Condition Nov 20, 20238 Natural Ways to Relieve Stress: An Ultimate Guide
Look into natural ways to relieve stress that work. Improve your sleep and exercise in your daily routine for a balanced life
-
 Fitness Jan 08, 2024
Fitness Jan 08, 2024The Role and Importance of Physical Therapy in Healthcare
Explore the benefits of physical therapy, learn how to get started, and understand the vital role of physical therapists in healthcare
